Junit5结合高级断言 hamcrest
JUnit5结合高级断言-hamcrest
pom文件导入:
pom 导入
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hamcrest</groupId>
<artifactId>hamcrest</artifactId>
<version>2.2</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
Hamcrest
-
Common Core Matchers- 常用断言
- is
- equalTo
- not
- hasItem
- allOf
- anyOf
- both
- either
常用的匹配器
JUnit 5 结合高级断言库 Hamcrest,可以提供更丰富的断言匹配器,以增强测试代码的可读性和可维护性。
is:用于检查对象是否等于指定值
-
is(T)- 将一个对象作为参数来检查相等性
-
is(Matcher<T>)- 使用另一个匹配器,使相等性语句更具表现力
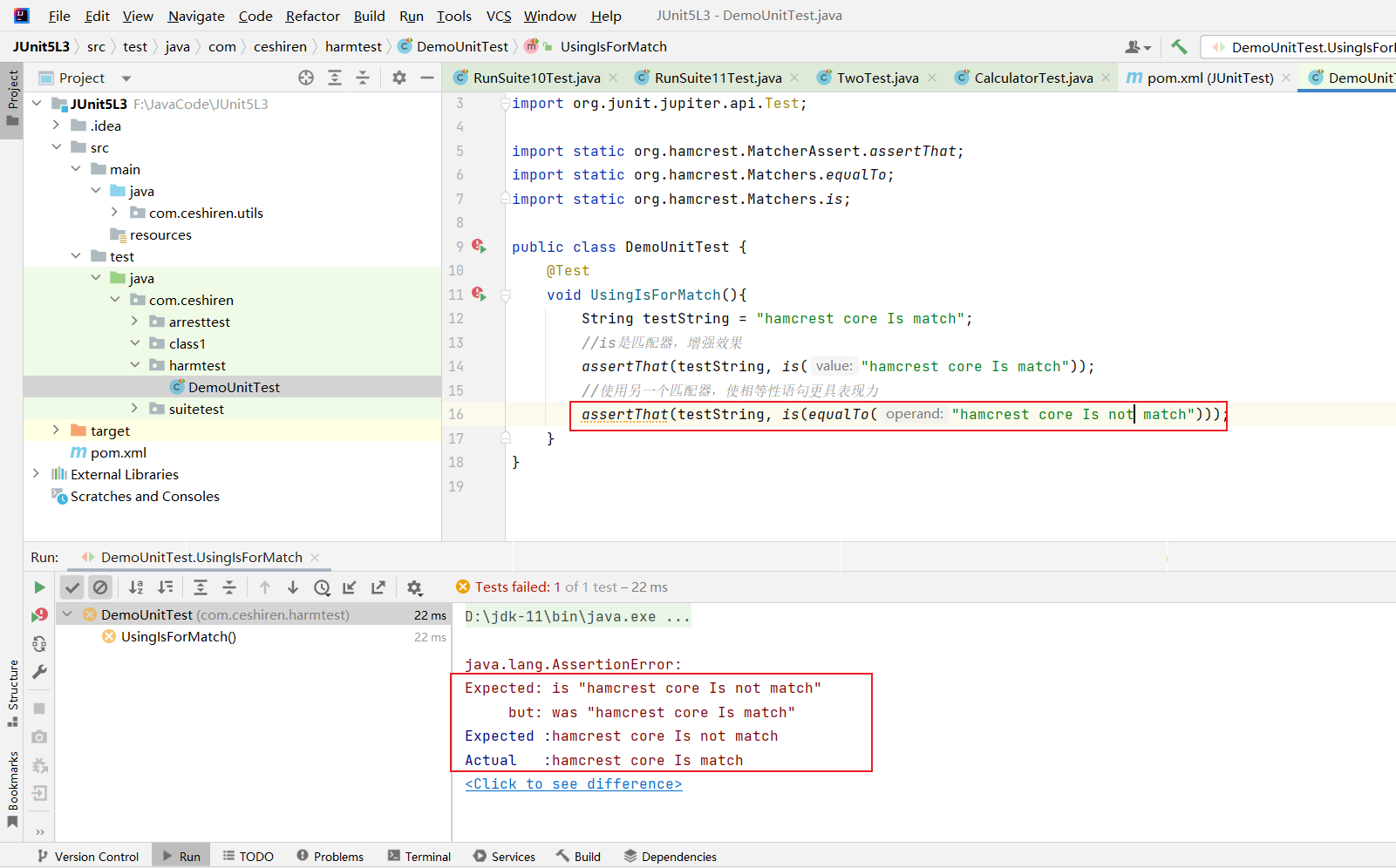
- 代码示例,这里的 assertThat、is、equalTo 均为
hamcrest模块中的,导入的时候需要注意。
@Test
void UsingIsForMatch(){
String testString = "hamcrest core Is match";
//is是匹配器,增强效果
assertThat(testString, is("hamcrest core Is match"));
//使用另一个匹配器,使相等性语句更具表现力
assertThat(testString, is(equalTo("hamcrest core Is not match")));
}
- 使用效果
equalTo(T):用于比较两个对象是否相等
- 将一个对象作为参数并检查其与另一个对象的相等性{style=width:500px}
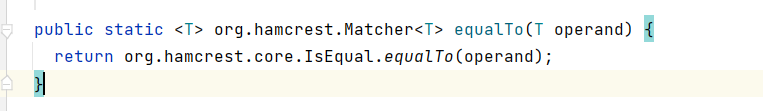
- 经常与
is(Matcher<T>)一起使用{style=width:500px} ctrl+鼠标点击equalTo可以查看对于 equalTo 的定义,从定义可以看出 equalTo 可以接收所有的泛型。
- 代码示例
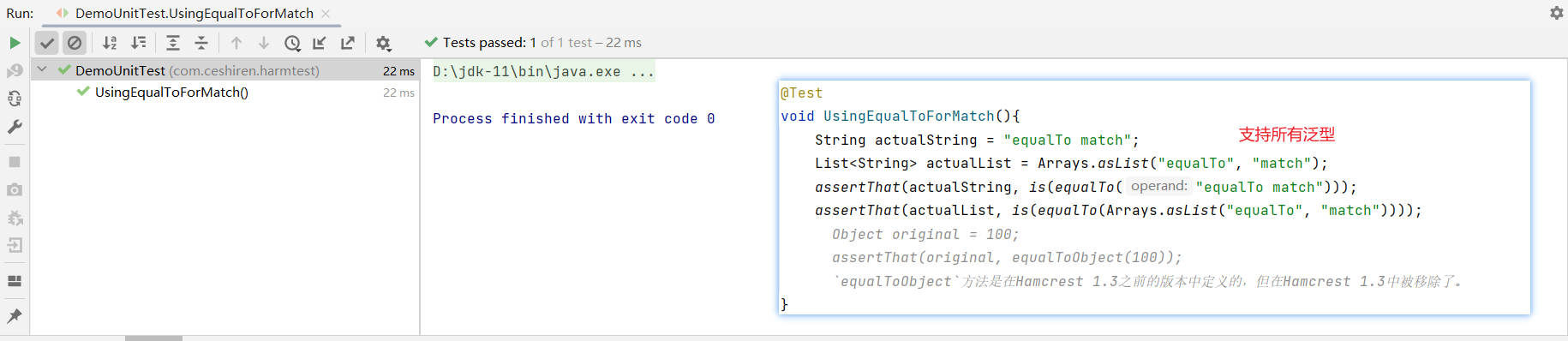
equalToObject方法是在 Hamcrest 1.3 之前的版本中定义的,新版本中被移除了。
@Test
void UsingEqualToForMatch(){
String actualString = "equalTo match";
List<String> actualList = Arrays.asList("equalTo", "match");
assertThat(actualString, is(equalTo("equalTo match")));
assertThat(actualList, is(equalTo(Arrays.asList("equalTo", "match"))));
// Object original = 100;
// assertThat(original, equalToObject(100));
// `equalToObject`方法是在Hamcrest 1.3之前的版本中定义的,但在Hamcrest 1.3中被移除了。
}
问题
- 使用效果
not:用于取反其他匹配器
not
- 检查给定对象的不相等性
-
not(T)- 接受一个对象作为参数
-
not(Matcher<T>)- 接受另一个匹配器
@Test
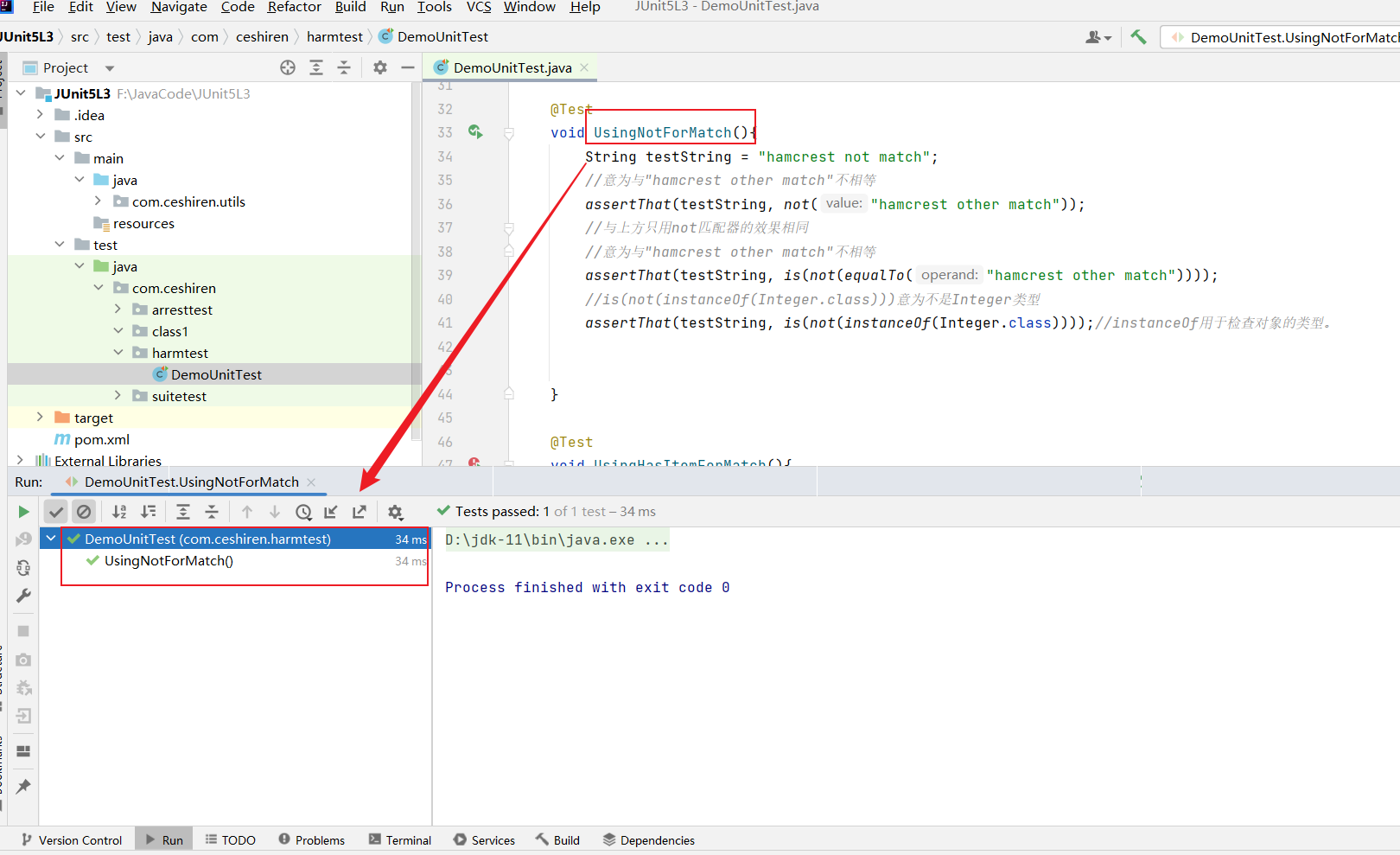
void UsingNotForMatch(){
String testString = "hamcrest not match";
//意为与"hamcrest other match"不相等
assertThat(testString, not("hamcrest other match"));
//与上方只用not匹配器的效果相同
//意为与"hamcrest other match"不相等
assertThat(testString, is(not(equalTo("hamcrest other match"))));
//is(not(instanceOf(Integer.class)))意为不是Integer类型
assertThat(testString, is(not(instanceOf(Integer.class))));//instanceOf用于检查对象的类型。
}
- 使用效果
hasItem:用于判断给定的集合或数组中是否包含特定的元素。
hasItem(T)T 为泛型
hasItem(Matcher<? extends T>)
- 检查的
Iterable集合是否与给定对象或匹配器匹配{style=width:500px}
- 也可以对多个项目进行断言{style=width:500px}
@Test
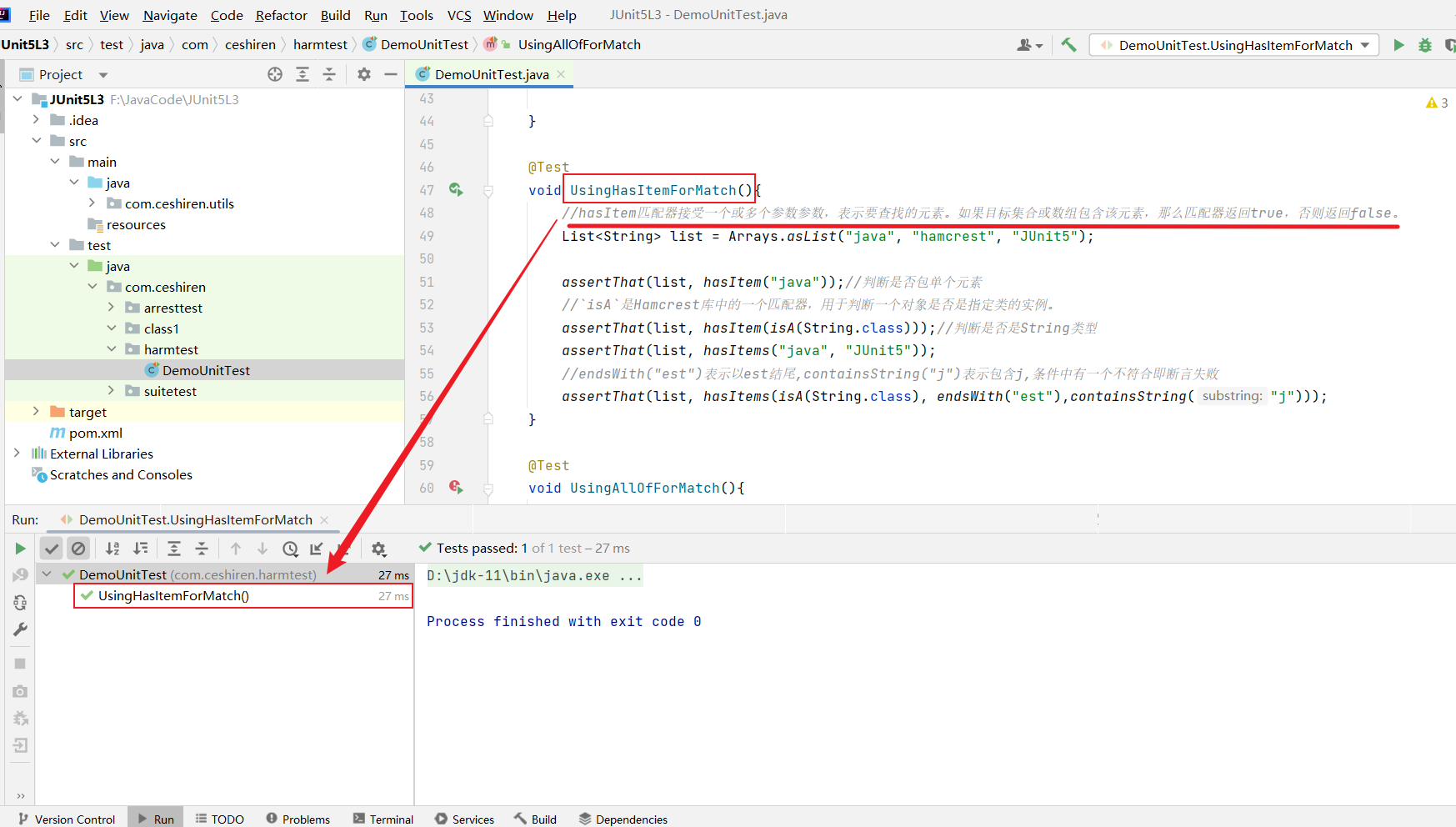
void UsingHasItemForMatch(){
//`hasItem`匹配器接受一个或多个参数参数,表示要查找的元素。如果目标集合或数组包含该元素,那么匹配器返回`true`,否则返回`false`。
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("java", "hamcrest", "JUnit5");
assertThat(list, hasItem("java"));//判断是否包单个元素
//`isA`是Hamcrest库中的一个匹配器,用于判断一个对象是否是指定类的实例。
assertThat(list, hasItem(isA(String.class)));//判断是否是String类型
assertThat(list, hasItems("java", "JUnit5"));
//endsWith("est")表示以est结尾,containsString("j")表示包含j,条件中有一个不符合即断言失败
assertThat(list, hasItems(isA(String.class), endsWith("est"),containsString("j")));
}
- 使用效果
allOf:接受一个或多个匹配器作为参数,并且要求所有的匹配器都满足条件
allOf(Matcher<? extends T>…)
- 断言实际对象是否与所有指定条件匹配{style=width:500px}
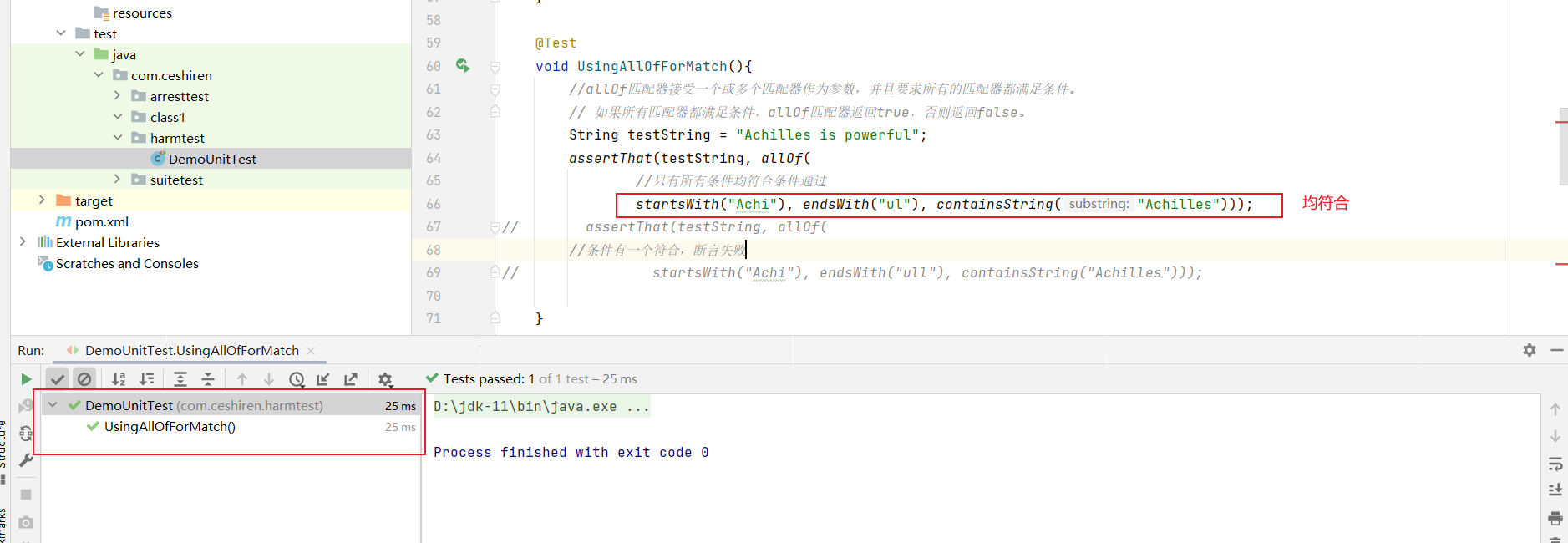
@Test
void UsingAllOfForMatch(){
//allOf匹配器接受一个或多个匹配器作为参数,并且要求所有的匹配器都满足条件。
// 如果所有匹配器都满足条件,allOf匹配器返回true,否则返回false。
String testString = "Achilles is powerful";
assertThat(testString, allOf(
//只有
startsWith("Achi"), endsWith("ul"), containsString("Achilles")));
}
- 使用效果:
- 条件全部符合,断言通过
- 条件有一个不符合,断言失败
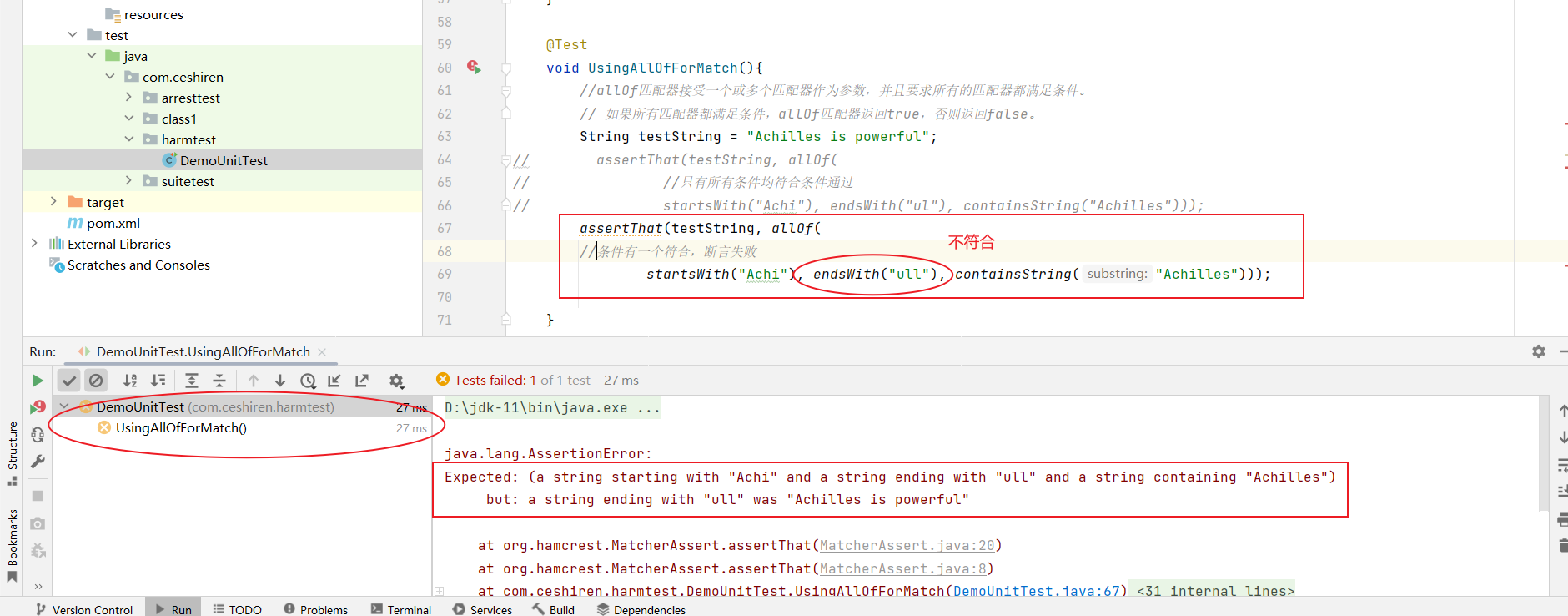
- 条件全部符合,断言通过
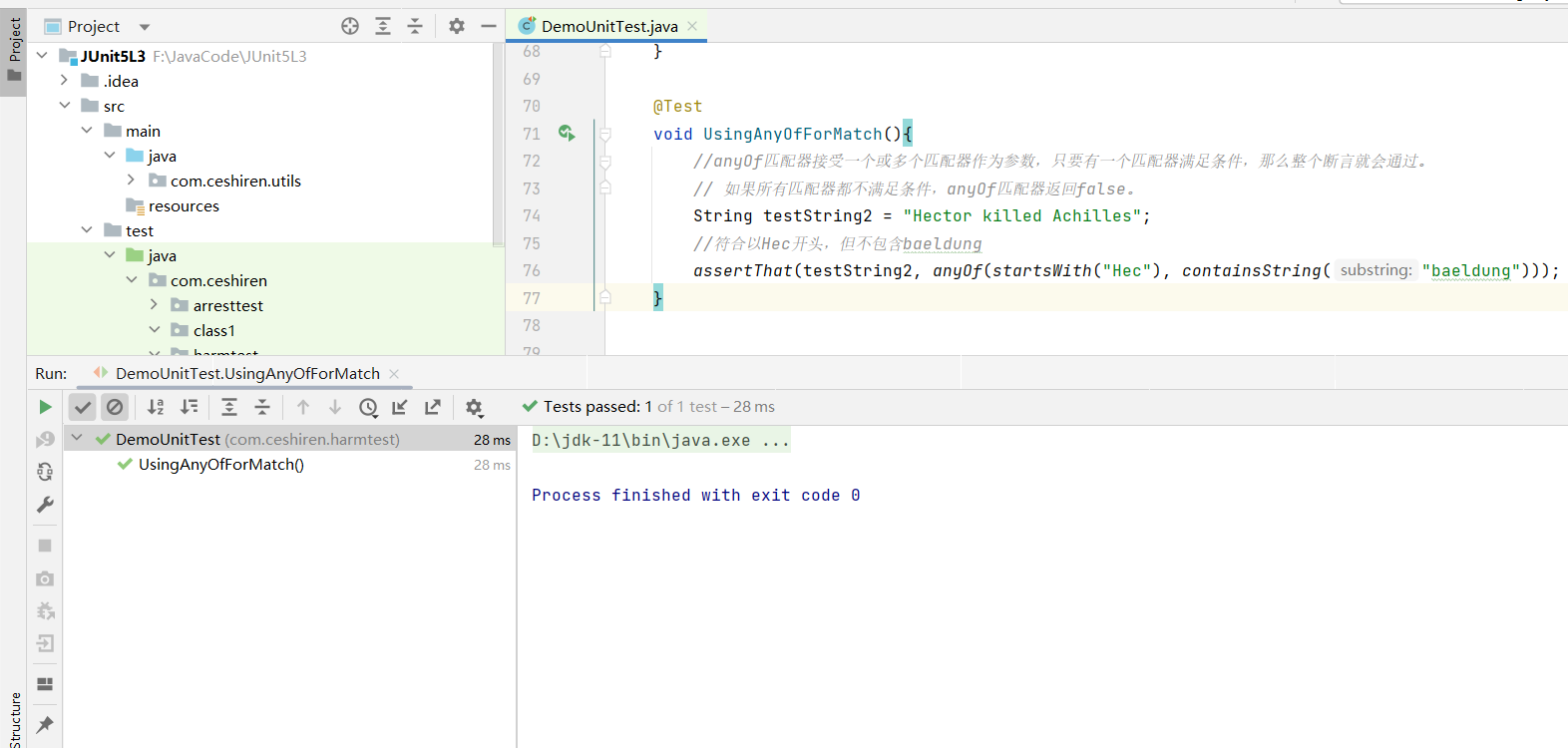
anyOf:接受一个或多个匹配器作为参数,只要有一个匹配器满足条件,那么整个断言就会通过
anyOf(Matcher<? extends T>…)
- 检查的对象匹配任何指定的条件,则匹配{style=width:500px}
@Test
void UsingAnyOfForMatch(){
//anyOf匹配器接受一个或多个匹配器作为参数,只要有一个匹配器满足条件,那么整个断言就会通过。
// 如果所有匹配器都不满足条件,anyOf匹配器返回false。
String testString2 = "Hector killed Achilles";
//符合以Hec开头,但不包含baeldung
assertThat(testString2, anyOf(startsWith("Hec"), containsString("baeldung")));
}
- 使用效果:条件只符合一个,断言通过
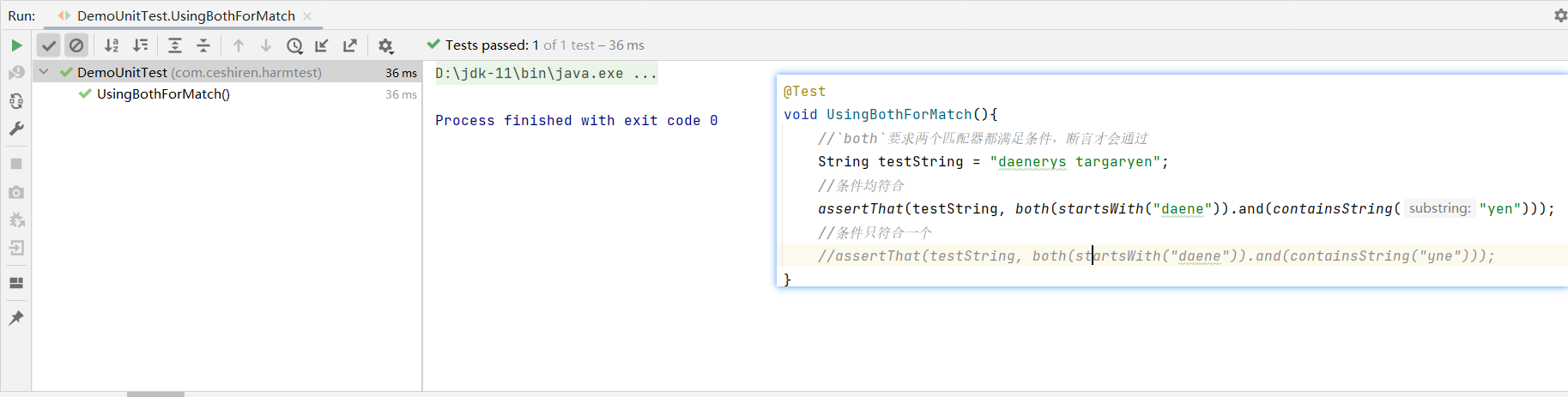
both:要求两个匹配器都满足条件
-
both(Matcher<? extends T>)- 和
and配合使用{style=width:500px}
- 和
- 两个指定条件都匹配检查对象时匹配{style=width:500px}
@Test
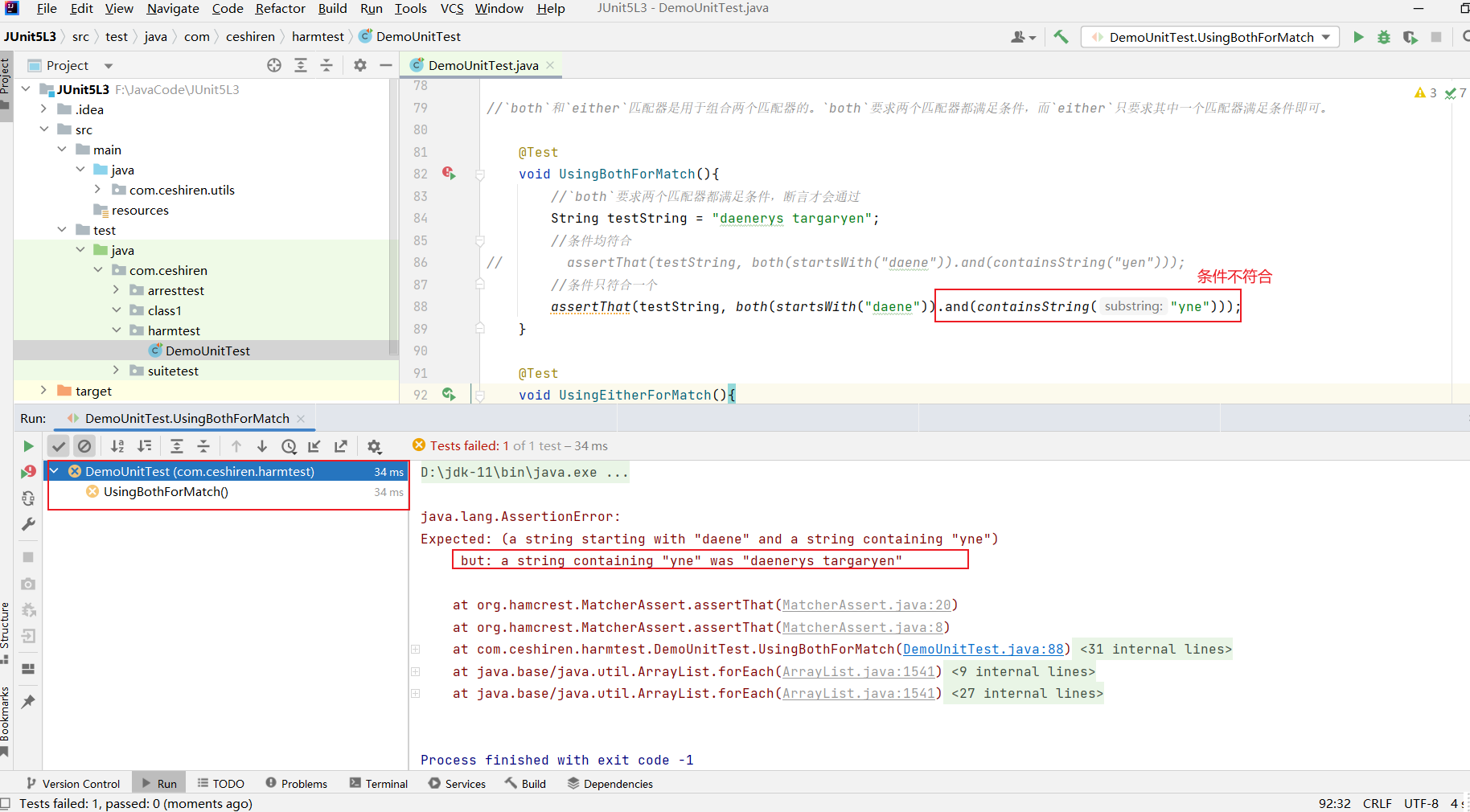
void UsingBothForMatch(){
//`both`要求两个匹配器都满足条件,断言才会通过
String testString = "daenerys targaryen";
//条件均符合
assertThat(testString, both(startsWith("daene")).and(containsString("yen")));
//条件只符合一个
//assertThat(testString, both(startsWith("daene")).and(containsString("yne")));
- 使用效果:条件都不符合或者只符合一个时断言不会通过
- 条件均符合,断言通过
- 条件只符合一个,断言未通过
- 条件均符合,断言通过
either:只要求其中一个匹配器满足条件即可
-
either(Matcher<? extends T>)- 和
or配合使用{style=width:500px}
- 和
- 任一指定条件与检查对象匹配时匹配{style=width:500px}
@Test
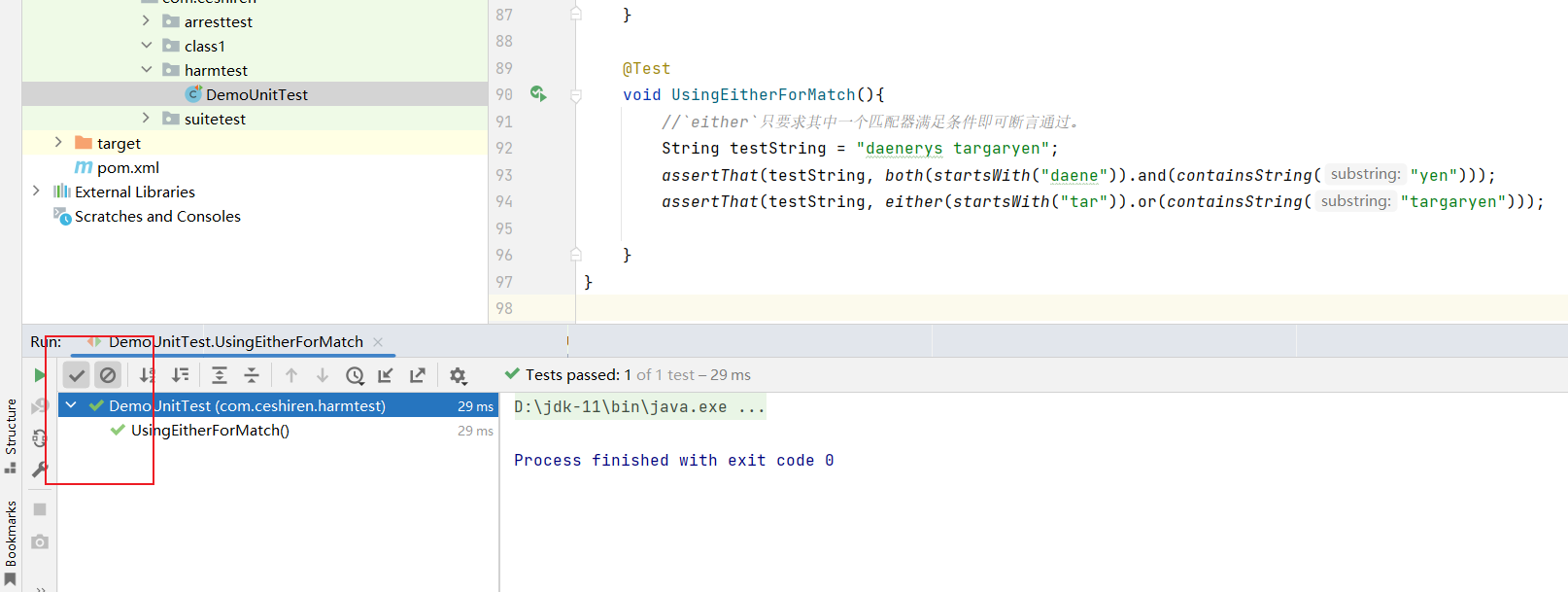
void UsingEitherForMatch(){
//`either`只要求其中一个匹配器满足条件即可断言通过。
String testString = "daenerys targaryen";
assertThat(testString, both(startsWith("daene")).and(containsString("yen")));
assertThat(testString, either(startsWith("tar")).or(containsString("targaryen")));
}
- 使用效果:
testString字符串中是以daene开头也包含yen,both 匹配器的条件都满足;使用并非是以tar开头,但包含targaryen,符合 either 匹配器中的条件之一,两条断言均通过。